Sharing notes from my ongoing learning journey — what I build, break and understand along the way.
Exploring Network Topologies: Bus, Star, Ring and More
What Is a Network Topology?
Recently, I started learning about computer networks, and one of the topics that really caught my attention was network topologies. These are basically the ways devices (like computers, printers, etc.) are connected to each other in a network. In this post, I’ll explain the most common types of network topologies, in a simple way, just as I understood them.
1. Bus Topology
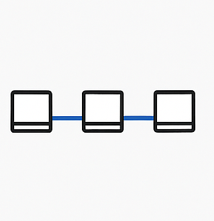
In a Bus topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, like a line.
- + Advantages: It’s cheap and simple to set up.
- – Disadvantages: If the main cable breaks, the whole network stops working.
Think of it like a single train track — if it breaks, no train can pass.
2. Star Topolog
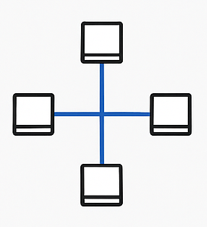
In a Star topology, all devices are connected to a central device (like a switch or hub).
- + Advantages: Easy to detect problems. If one device fails, the others still work.
- – Disadvantages: If the central device fails, the entire network goes down.
It’s like a wheel — the hub is in the center, and all spokes (devices) connect to it.
3. Ring Topology
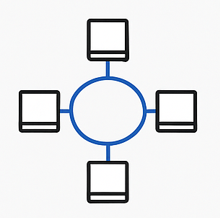
In a Ring topology, each device connects to two other devices, forming a ring.
- + Advantages: Data moves in one direction, so there are fewer data collisions.
- – Disadvantages: If one connection breaks, the whole network can stop.
Like a circle of friends passing a message only one way.
4. Mesh Topology
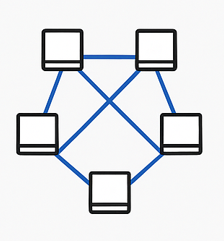
In a Mesh topology, each device connects to many (or all) other devices.
- + Advantages: Very reliable. If one path fails, data can use another.
- – Disadvantages: Expensive and complex to set up.
This is used in places where reliability is super important, like military systems.
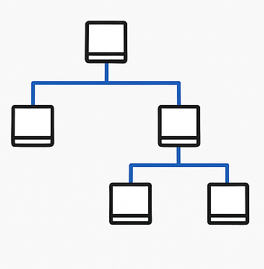
5. Tree Topology
Tree topology is a mix of star and bus topologies. It has groups of star networks connected to a central bus line.
- + Advantages: Good for large networks with layers.
- – Disadvantages: Can be hard to manage and troubleshoot.
Just like a real tree — it has a trunk (main cable) and branches (star groups).
Comparison Table
| Topology | Pros | Cons | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | Simple, cheap | One cable failure stops everything | Old small networks |
| Star | Easy to manage | Center failure affects all | Homes, offices |
| Ring | Data control | Sensitive to breaks | Some fiber networks |
| Mesh | Very reliable | Expensive, complex | Military, critical systems |
| Tree | Scalable | Can be complex | Large buildings, schools |
Final Thoughts
Understanding network topologies helped me realize how data travels between devices and why the design of a network matters. I found that Star topology is the most common today, especially in home and office networks.
I’m still learning, but explaining it like this really helps me remember better. I hope it helps you too!
