Sharing notes from my ongoing learning journey — what I build, break and understand along the way.
What Is the Difference Between Client and Server in Web Development?
Client vs Server: What Do They Mean in Web Development?
When stepping into the world of web development, one of the first concepts you’ll encounter is the distinction between a “client” and a “server.” These two components form the backbone of all web-based communication. Websites, apps, services — they all function thanks to this interaction.
Understanding this separation is not only crucial for developers but also for anyone curious about how the internet works.
What Is a Client?
A client is any device or software (usually a web browser) that initiates a request. Its job is to send a user action to the server and display the server’s response back to the user.
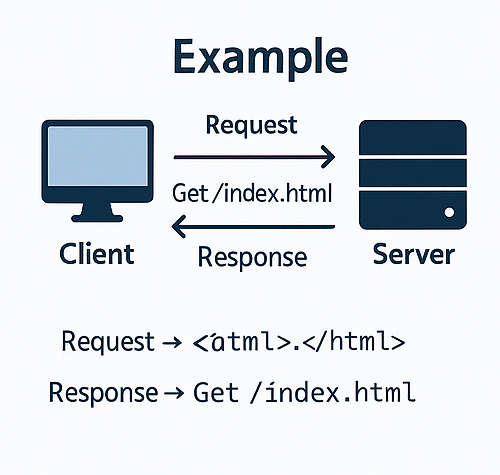
Example:
When you type www.example.com into your browser, the browser (client) sends a request to the server asking for that page.
What Is a Server?
A server is a remote machine (usually hosted on the cloud or in a data center) that listens for requests and sends back appropriate responses. It might retrieve a static HTML file, process dynamic content, or query a database — depending on the need.
Example:
The server for www.example.com receives the request, finds the corresponding HTML file, and sends it back to your browser.
Client vs Server Comparison
| Feature | Client | Server |
|---|---|---|
| Location | User’s device | Remote machine / hosting environment |
| Task | Sends requests, renders content | Processes requests, sends responses |
| Technologies Used | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | PHP, Python, Node.js, SQL |
| Resource Usage | Usually light (UI, display) | Heavier (data processing, logic, DB) |
| User Access | Directly accessed by user | Works behind the scenes |
Frontend vs Backend
The client-server model also reflects the frontend vs backend structure in modern development:
- Frontend (Client-Side):
This includes everything the user sees — layout, buttons, forms — built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. - Backend (Server-Side):
Handles database queries, logic, APIs, authentication, and everything else the user doesn’t see.
Example:
A user submits a signup form:
- The form design and interaction happen on the frontend
- Saving the data to a database happens on the backend
How Do They Communicate? (HTTP Process)
- User types a web address in the browser
- Browser gets the IP address via DNS
- An HTTP or HTTPS request is sent to the server
- Server processes the request and prepares a response
- Server sends back the requested file or data
- Browser renders the response for the user
This cycle happens in milliseconds — yet powers everything we do on the internet.
In Short
The client-server model is the foundation of the internet as we know it. From simple websites to complex cloud apps and APIs — they all operate through this communication.
Understanding it will not only boost your web development knowledge but also give you a clear framework for learning backend, frontend, and full-stack technologies.
